How to Switch to Proper Nutrition: Key Principles
Making the shift to proper nutrition is one of the most rewarding lifestyle changes you can undertake. A balanced diet fuels your body, supports mental clarity, and enhances your overall quality of life. While the transition might seem daunting at first, understanding the key principles of healthy eating simplifies the process and sets the foundation for lasting success. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential steps to help you adopt a balanced and nourishing diet.
The Importance of Hydration and Whole Foods
1. Hydration is Essential: Water as the Foundation of Health
Before you even consider what’s on your plate, it’s crucial to address hydration. Water plays a vital role in nearly every bodily function, from digestion to temperature regulation. Staying hydrated not only supports physical health but also impacts mental well-being.
Why Hydration Matters:
Supports Digestion: Water aids in breaking down food and absorbing nutrients.
Flushes Out Toxins: Proper hydration helps the kidneys filter waste efficiently.
Regulates Mood and Energy: Dehydration can lead to fatigue and irritability.
Weight Management: Drinking water before meals can reduce hunger, preventing overeating.
How Much Water Should You Drink?
The general recommendation is 8 glasses of water per day (about 2 liters). However, your needs may vary depending on activity level, climate, and individual health. Carry a reusable water bottle to make hydration a consistent habit.
Pro Tip: Add a slice of lemon, cucumber, or mint to your water for a refreshing flavor boost that encourages you to drink more.
2. Focus on Whole Foods: The Backbone of a Healthy Diet
Whole foods—those that are minimally processed and close to their natural state—should form the foundation of your meals. These foods are nutrient-dense and free from unhealthy additives commonly found in processed items.
Examples of Whole Foods:
Fruits and Vegetables: Fresh or frozen, these should be staples in your diet.
Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole-grain bread.
Lean Proteins: Chicken, fish, tofu, legumes, and eggs.
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, and walnuts for healthy fats and protein.
Why Whole Foods Matter:
Nutrient Density: Whole foods are rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Health Benefits: They reduce the risk of chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes.
Sustained Energy: Unlike processed foods, whole foods provide steady energy without sugar crashes.
How to Incorporate Whole Foods:
Start by replacing one processed item in your daily routine with a whole-food alternative. For example:
Swap sugary cereals for oatmeal topped with fresh fruit.
Replace white bread with whole-grain options.
3. Incorporate More Fruits and Vegetables: Nature’s Powerhouses
Fruits and vegetables are packed with essential nutrients and antioxidants that support your body’s defense systems. They’re also versatile, delicious, and accessible for every meal.
Why They’re Essential:
Vitamins and Minerals: Rich in vitamin C, potassium, folate, and more.
Antioxidants: Help combat inflammation and oxidative stress.
Fiber: Promotes healthy digestion and supports weight management.
How Much Should You Eat?
The general guideline is 5 servings of fruits and vegetables daily, with each serving roughly equivalent to one cup. Aim to fill half your plate with produce at each meal.
Practical Tips to Add More Produce:
Add spinach or kale to smoothies for a nutrient boost.
Snack on raw veggies like carrots or cucumber with hummus.
Roast a variety of vegetables with olive oil, garlic, and herbs for a flavorful side dish.
Pro Tip: Keep fruits and vegetables visible and accessible in your kitchen to encourage healthy snacking.

Balancing Macronutrients and Practicing Portion Control
Transitioning to proper nutrition involves more than just what you eat; it’s about how you balance your meals and manage portions. The right combination of macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—ensures your body receives the fuel it needs for optimal performance. Coupled with mindful portion control, these principles empower you to maintain a sustainable and healthy diet without feeling deprived.
1. Balance Your Macronutrients: The Key to a Well-Rounded Diet
Each macronutrient plays a unique and vital role in your body’s health and functionality. Striking the right balance among these components is essential for energy, muscle growth, and overall well-being.
Understanding Macronutrients
Carbohydrates: Your body’s primary energy source. Opt for complex carbs, such as whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables, as they provide sustained energy and are rich in fiber.
Proteins: Crucial for muscle repair, hormone production, and immune health. Incorporate both plant-based (e.g., lentils, chickpeas, tofu) and animal-based proteins (e.g., lean meat, fish, eggs).
Fats: Healthy fats support brain function, hormone production, and nutrient absorption. Focus on unsaturated fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel).
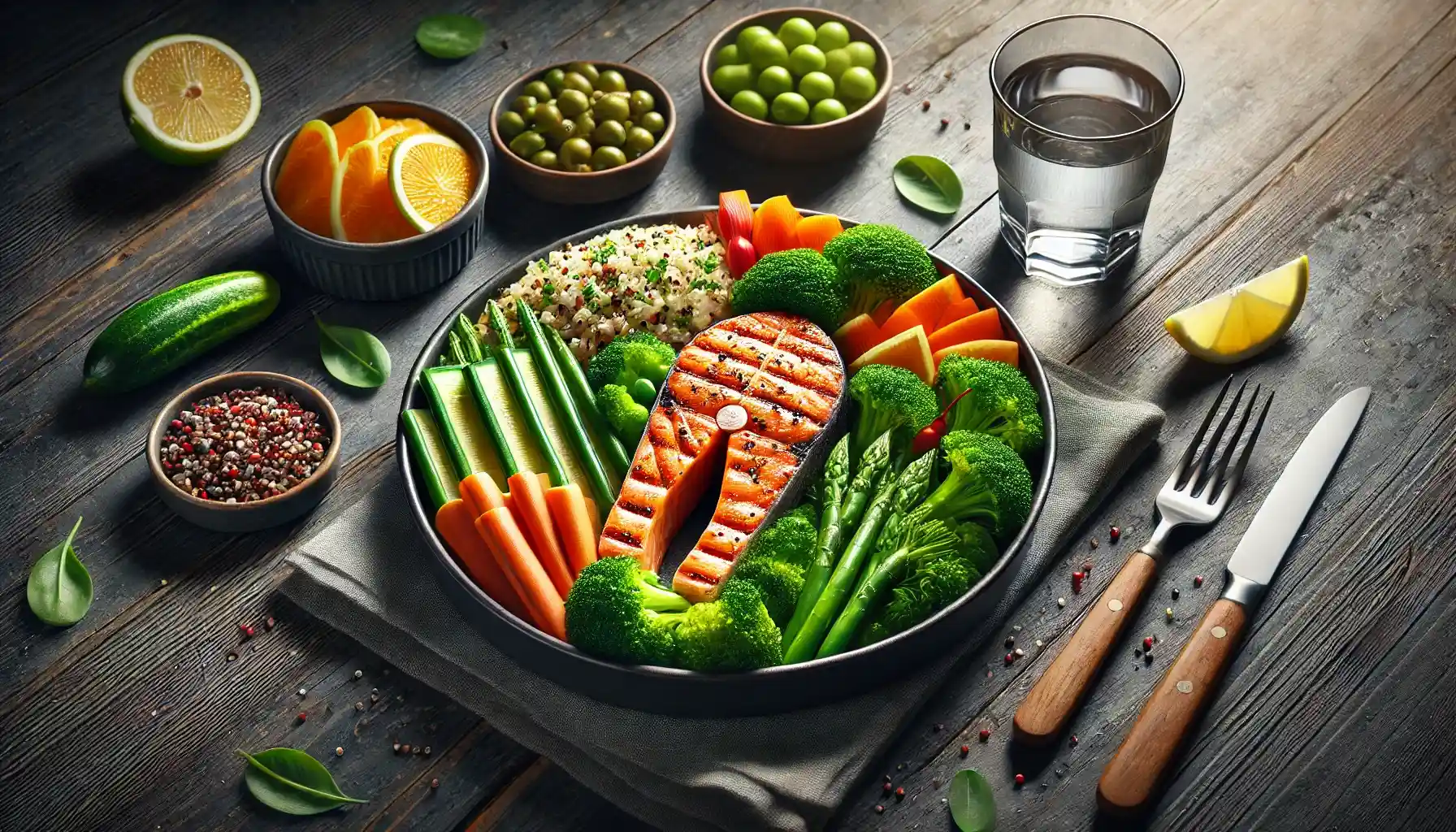
Building a Balanced Plate
A balanced meal typically includes all three macronutrients in appropriate proportions:
Carbs (40–50%): Think brown rice, quinoa, or sweet potatoes.
Proteins (25–30%): Choose lean meats, beans, or plant-based protein.
Fats (20–30%): Incorporate olive oil, nuts, or avocado.
Pro Tip: Use the "plate method" as a visual guide—half your plate should be fruits and vegetables, a quarter lean protein, and a quarter whole grains or starchy vegetables.
Examples of Balanced Meals
Breakfast: Oatmeal topped with chia seeds, almond butter, and fresh berries.
Lunch: Grilled chicken breast, roasted sweet potatoes, and steamed broccoli.
Dinner: Salmon with quinoa, asparagus, and a drizzle of olive oil.
2. Practice Portion Control: Avoid Overeating Without Feeling Deprived
Portion control is critical for managing calorie intake and preventing the consumption of excess food, even if it’s healthy. Learning to recognize proper portion sizes helps maintain a balanced diet and supports weight management goals.
Why Portion Control Matters
Prevents overeating, especially with calorie-dense foods.
Helps regulate energy levels throughout the day.
Encourages mindfulness and reduces food waste.
Portion Control Techniques
Use Smaller Plates: Swap large dinner plates for smaller ones to create the illusion of a fuller plate.
Measure Serving Sizes: Use measuring cups, a food scale, or visual cues (e.g., a fist-sized portion of carbs or a palm-sized serving of protein).
Serve Mindfully: Pre-portion snacks or meals to avoid overeating straight from the package or pot.
The Role of Frequency and Timing
Eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can help maintain energy levels and prevent overeating at main meals.
Benefits:
Stabilizes blood sugar levels.
Reduces hunger-induced binge eating.
Supports digestion.
Pro Tip: Aim for three balanced meals and two snacks daily, spacing them 3–4 hours apart.
3. Limit Added Sugars and Saturated Fats
Even with balanced macronutrients and portion control, certain dietary components should be minimized for optimal health. Reducing added sugars and saturated fats is key to maintaining heart health and managing weight.
Cut Back on Added Sugars
Added sugars contribute empty calories with no nutritional benefit. Overconsumption can lead to weight gain, energy crashes, and an increased risk of chronic diseases like diabetes.
Sources to Watch For:
Sugary beverages (sodas, flavored coffees, energy drinks).
Packaged snacks (cookies, candies, granola bars).
Condiments (ketchup, barbecue sauce, salad dressings).
How to Reduce Added Sugars:
Opt for unsweetened alternatives (e.g., unsweetened almond milk).
Sweeten naturally with fresh fruit or small amounts of honey.
Read labels for hidden sugars listed as “corn syrup,” “fructose,” or “sucrose.”
Choose Healthy Fats Over Saturated Fats
Saturated fats, often found in processed and fried foods, can raise cholesterol levels and increase heart disease risk. Replace these with healthier options:
Unhealthy Sources: Butter, high-fat meats, cheese, and fast food.
Healthy Alternatives: Olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
Pro Tip: If cooking with oils, stick to olive oil or avocado oil, which contain heart-healthy monounsaturated fats.
4. Cook at Home More Often: Take Control of Your Nutrition
One of the most effective ways to ensure you’re eating balanced, portion-controlled meals is by preparing them yourself. Cooking at home allows you to choose quality ingredients and avoid unnecessary additives.
Benefits of Cooking at Home
Portion Control: You decide how much to serve and eat.
Ingredient Transparency: You know exactly what goes into your food.
Cost Savings: Preparing meals at home is often more economical than dining out.
Skill Development: Cooking builds confidence and encourages experimentation with healthy recipes.
How to Start Cooking More
Begin Gradually: Start with two or three home-cooked meals per week and increase over time.
Meal Prep: Dedicate a day to prepping meals and snacks for the week to save time and reduce stress.
Stock Your Pantry: Keep essentials like whole grains, canned beans, spices, and frozen vegetables on hand for quick, nutritious meals.
Pro Tip: Explore simple recipes with minimal ingredients to build your confidence in the kitchen.
The Role of Sleep, Stress Management, and Mindful Eating
Proper nutrition goes beyond just the food on your plate. Sleep, stress management, and mindfulness are critical factors that influence how your body processes and benefits from the nutrients you consume. By addressing these aspects, you can create a holistic approach to healthy living and sustain your journey toward proper nutrition.
1. Prioritize Sleep: The Unsung Hero of Nutrition
Sleep is often overlooked in the pursuit of better health, but its impact on nutrition and overall well-being is profound. Adequate sleep not only supports a healthy metabolism but also regulates hunger hormones and boosts energy levels.
Why Sleep is Crucial
Regulates Hunger Hormones: Poor sleep increases ghrelin (hunger hormone) and decreases leptin (fullness hormone), leading to overeating.
Supports Metabolism: Sleep deprivation can slow metabolic function, making it harder to maintain a healthy weight.
Improves Decision-Making: A well-rested mind is more likely to make healthy food choices.
How to Improve Sleep Quality
Establish a Routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same time daily, even on weekends.
Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Keep your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool.
Limit Screen Time: Avoid screens at least one hour before bed to reduce blue light exposure.
Watch What You Eat: Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol in the hours leading up to bedtime.
Pro Tip: Aim for 7–9 hours of sleep per night to optimize your body’s recovery and nutritional balance.
2. Manage Stress: A Key to Reducing Emotional Eating
Stress is a major factor in unhealthy eating habits, often leading to cravings for sugary or fatty foods. Learning to manage stress effectively can help you maintain control over your diet and improve overall health.
How Stress Affects Nutrition
Triggers Emotional Eating: Stress increases cortisol levels, which can lead to cravings for high-calorie comfort foods.
Disrupts Digestion: Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health and nutrient absorption.
Reduces Energy: High stress levels often result in fatigue, leading to skipped meals or reliance on convenience foods.
Techniques for Stress Management
Practice Mindfulness: Engage in activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing to calm your mind.
Stay Active: Regular exercise helps reduce stress and boosts endorphin levels.
Connect with Others: Talk to friends, family, or a therapist to manage stress more effectively.
Set Boundaries: Learn to say no to commitments that overwhelm you.
Pro Tip: Pair stress management with a balanced diet rich in magnesium (e.g., leafy greens, nuts) to help reduce anxiety.
3. Embrace Mindful Eating: Building a Healthy Relationship with Food
Mindful eating is about focusing on the present moment while consuming food, cultivating awareness of your body’s hunger and fullness cues. This practice not only enhances your enjoyment of meals but also supports better digestion and portion control.
Benefits of Mindful Eating
Prevents Overeating: Paying attention to hunger cues helps you avoid consuming more than your body needs.
Enhances Digestion: Eating slowly and savoring each bite improves digestion and nutrient absorption.
Encourages Gratitude: Focusing on the flavors and origins of your food fosters a deeper appreciation for your meals.
How to Practice Mindful Eating
Eliminate Distractions: Avoid eating in front of screens or while multitasking.
Eat Slowly: Chew thoroughly and take small bites to savor flavors and textures.
Check Hunger Levels: Pause halfway through your meal to assess if you’re still hungry.
Engage Your Senses: Pay attention to the smell, taste, and appearance of your food.
Portion Thoughtfully: Serve smaller portions and allow yourself to go back for more if needed.
Pro Tip: Keep a food journal to reflect on your eating habits and identify patterns that can be adjusted for better nutrition.
4. Build Consistency with Healthy Habits
Creating a sustainable routine is the ultimate goal of transitioning to proper nutrition. Small, consistent changes add up over time, leading to long-lasting results.
Steps to Build Consistency
Set Realistic Goals: Start with achievable changes, like drinking more water or adding one vegetable to your meals daily.
Track Progress: Use a journal, app, or calendar to monitor your successes and challenges.
Reward Yourself: Celebrate milestones with non-food rewards, like a new book or fitness gear.
Stay Flexible: Life happens—allow room for occasional indulgences without guilt.
Leverage the Power of Preparation
Preparation is key to maintaining consistency, especially during busy days.
Meal Prep: Dedicate one day a week to cooking and portioning meals for easy access.
Stock Healthy Snacks: Keep items like nuts, fruit, or yogurt on hand to curb hunger between meals.
Plan Ahead: Review your schedule and plan meals or snacks accordingly to avoid relying on fast food or convenience options.
Pro Tip: Involve family or friends in your healthy eating journey for added accountability and motivation.

Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Proper Nutrition
Switching to proper nutrition is a multifaceted journey that requires attention to your physical, emotional, and mental well-being. By prioritizing sleep, managing stress, and practicing mindful eating, you complement the dietary changes needed to achieve a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
Combining these principles with hydration, whole foods, portion control, and home cooking ensures a sustainable and enjoyable approach to nutrition. Remember, transitioning to a healthier diet isn’t about perfection—it’s about progress. Celebrate each step forward, and trust that consistency will lead to lasting benefits for your body and mind.
Your journey to proper nutrition begins with small, intentional changes. Embrace them, and watch as they transform your health and overall quality of life.